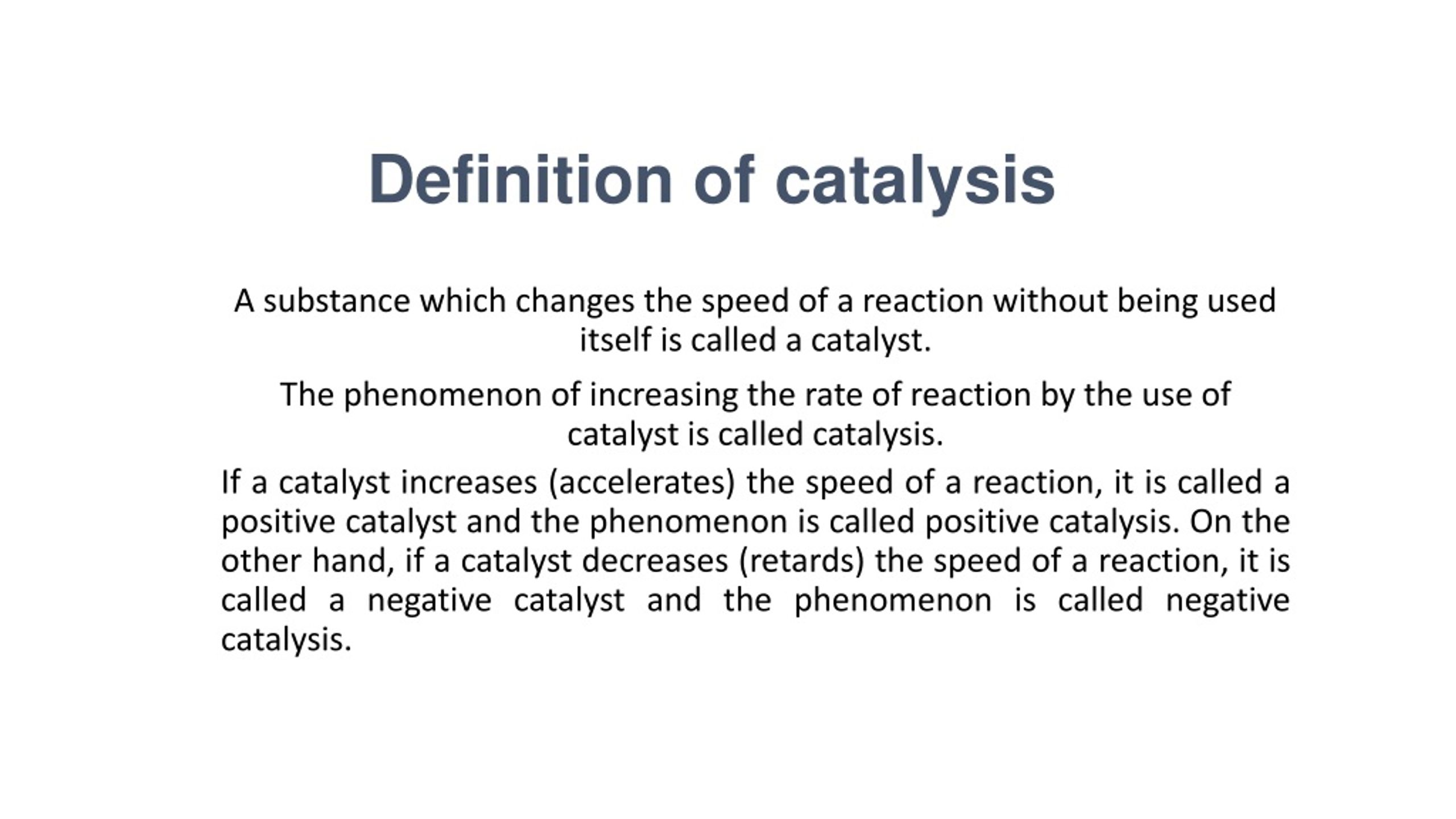
Catalyst Biology Terms . explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. A substance that helps a. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors.
from exozpzccv.blob.core.windows.net
an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. A substance that helps a. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,.
Catalyst Biology Simple Definition at Lydia Hatcher blog
Catalyst Biology Terms thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. A substance that helps a. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered.
From slidetodoc.com
ENZYME BIOLOGICAL CATALYST Enzyme As Catalyst All enzymes Catalyst Biology Terms A substance that helps a. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.pinterest.ca
Catalyst and Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis Enzymes, Chemistry, Active Catalyst Biology Terms explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From slideplayer.com
Catalysis Catalyst A substance that speeds up a reaction without being Catalyst Biology Terms thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.researchgate.net
Types of biological catalysts. A represents the reactant, and B Catalyst Biology Terms thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Chapter 8 enzymes biological catalyst Studypool Catalyst Biology Terms explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. a fundamental task of proteins is to act. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.pinterest.com.au
Biological catalysts Enzymes IGCSE Biology. ppt download Chemical Catalyst Biology Terms explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. an enzyme is a substance that acts as. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From exowzdqkr.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Image at Anna Schofield blog Catalyst Biology Terms an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. A substance that helps a. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Discuss enzyme regulation by. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Reaction Rate PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3534068 Catalyst Biology Terms catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. A substance that helps a. . Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.scribd.com
Biological Catalysts (13) Hydrolysis Enzyme Catalyst Biology Terms the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. Discuss enzyme regulation. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CATALYSIS AND CATALYTIC REACTION MECHANISM PART 1 PowerPoint Catalyst Biology Terms the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. A substance that helps a. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,”. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From exowzdqkr.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Image at Anna Schofield blog Catalyst Biology Terms an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. the. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT AP BIOLOGY CatalysT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Catalyst Biology Terms A substance that helps a. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. an enzyme is a substance that acts as. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From exozpzccv.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Simple Definition at Lydia Hatcher blog Catalyst Biology Terms An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed.. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From exozpzccv.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Simple Definition at Lydia Hatcher blog Catalyst Biology Terms An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. an enzyme. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.expii.com
Catalysts (Enzymes) — Overview & Examples Expii Catalyst Biology Terms the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. An entity (organic, inorganic, organometallic, protein or rna) that increases the rate of a reaction without itself. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. thanks to. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From www.slideshare.net
Biology 2.4 Catalyst Biology Terms Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. A substance that helps a. thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From eduinput.com
Biological CatalystEnzyme Nomenclature of Enzyme Catalyst Biology Terms explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. the biochemical processes induced by enzymes fall into broad classifications, such as hydrolysis,. a fundamental task of proteins. Catalyst Biology Terms.
From cemwppzp.blob.core.windows.net
What Are Catalysts In Biology at Marguerite Wiliams blog Catalyst Biology Terms thanks to catalysis, reactions that can take hundreds of years to complete in the uncatalyzed “real world,” occur in seconds in the presence of a. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered. A substance that helps a. explain how. Catalyst Biology Terms.